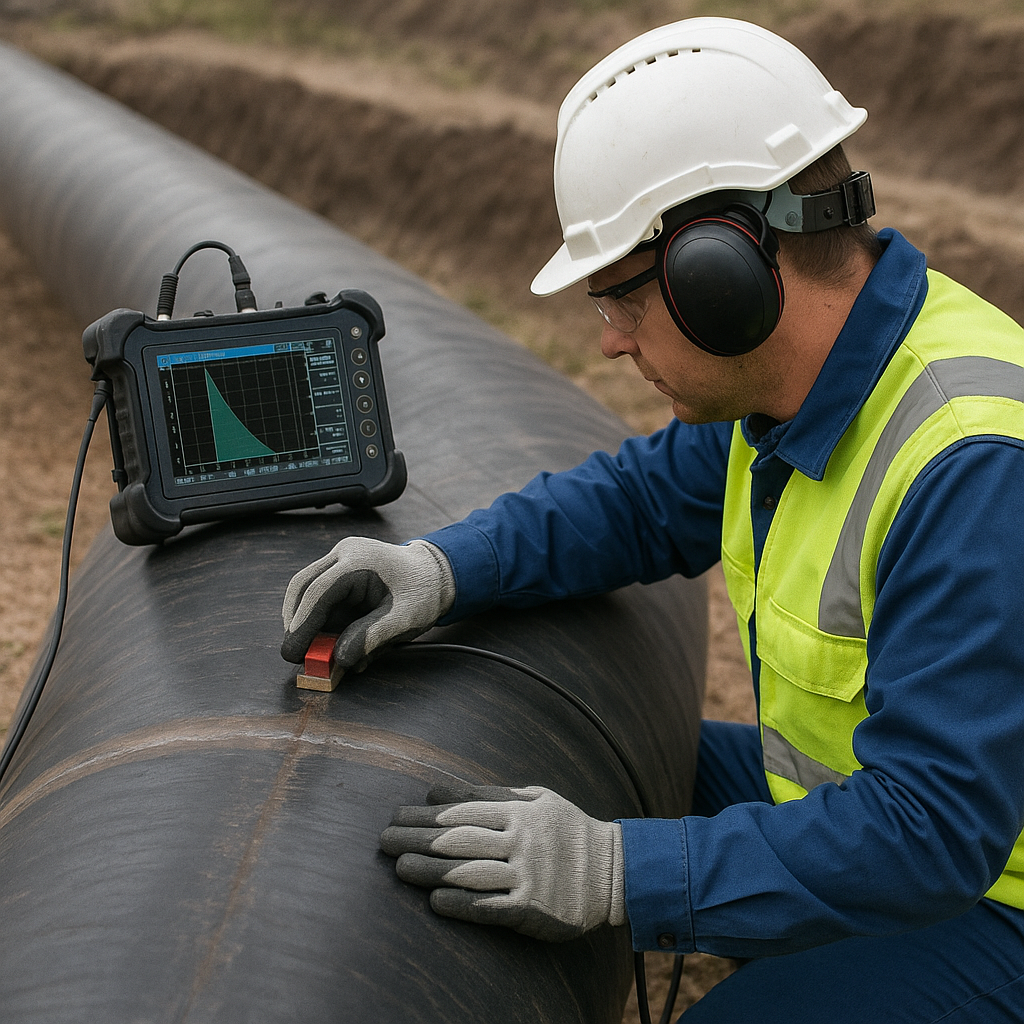
Pipeline inspection is essential to maintain the safety and efficiency of newly constructed or modified pipelines. This process includes various stages such as commissioning, commissioning and decommissioning.
During these stages, the pipeline is tested, cleaned, and prepared for operation. Removing contaminants such as oil, dirt, and grease is essential to prevent operational problems and hazardous situations.
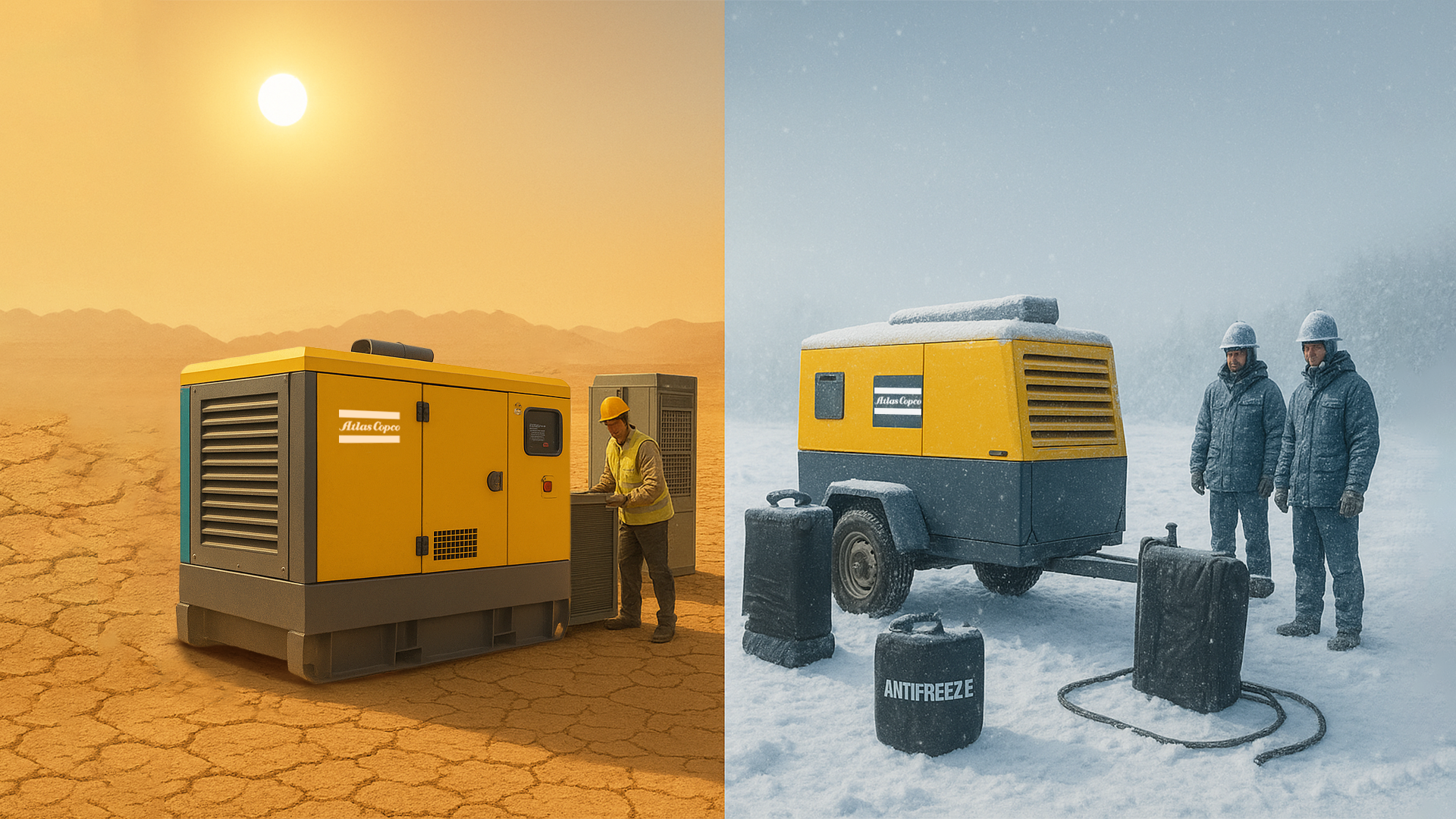
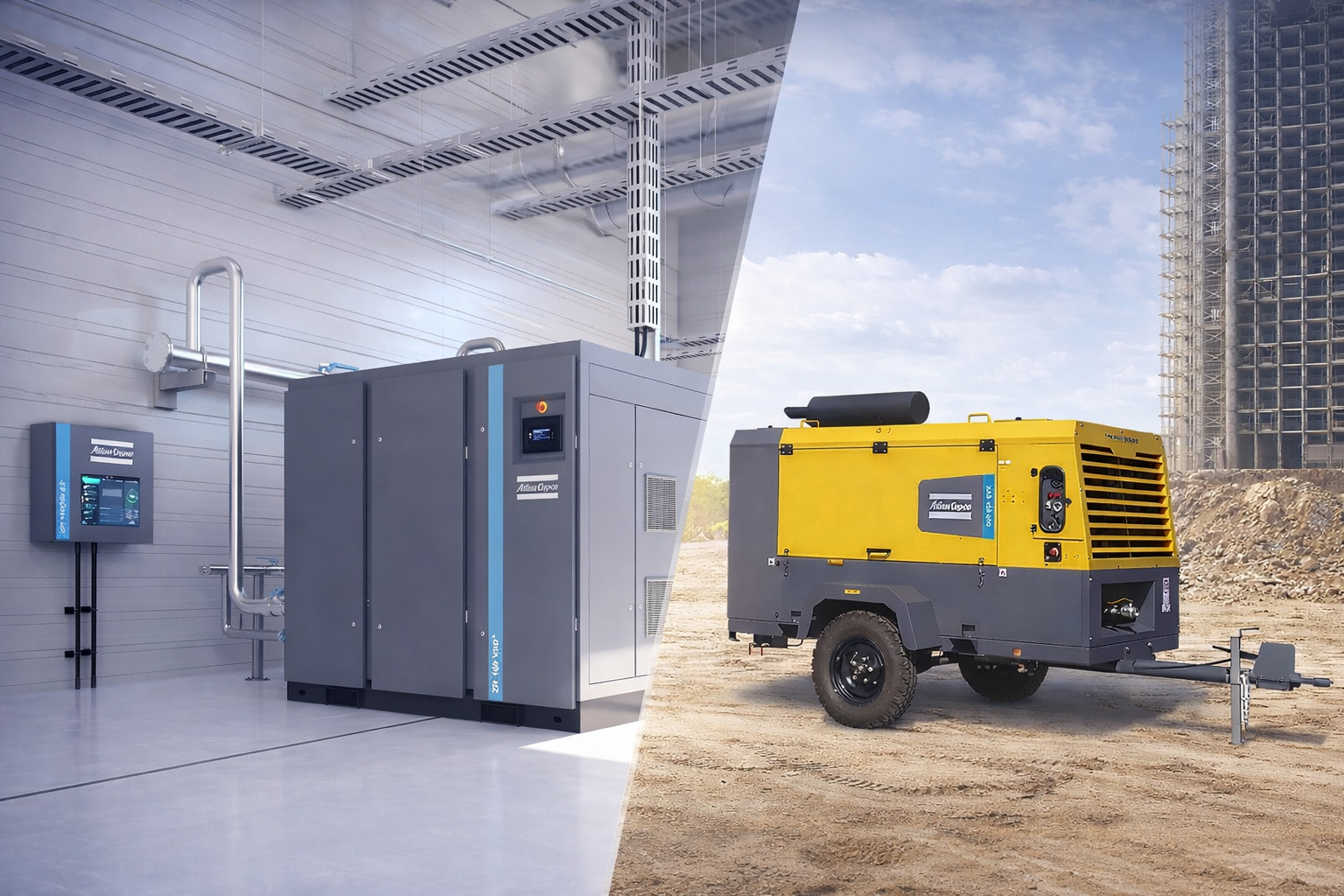
Specialized equipment such as portable air compressors, portable desiccant air dryers, high-pressure boosters, and nitrogen generators are often used to ensure thorough and safe inspection of pipelines.
Pipeline inspection stages
1. Initial commissioning
The first phase of pipeline inspection is called pre-commissioning . This involves conducting quality inspections and tests to ensure that the pipelines meet industry standards before normal operations begin. Key activities in this phase include safety This includes briefings on safety regulations , testing of safety equipment, and checking that all personnel have the necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to mitigate risks.
Portable air compressors play a vital role in this phase to thoroughly clean the pipelines. They help remove any debris or moisture left over from the construction phase, providing a clean slate before operations begin.
2. Commissioning
Commissioning is the next step in preparing a pipeline for operation. It involves the introduction of oil and gas products into the pipeline and carrying out detailed inspections using checklists to ensure that everything is satisfactory. This stage involves a series of procedures and tests to clean the pipeline and ensure that it meets safety, reliability and efficiency standards. Compliance with safety standards and quality requirements is checked and all equipment specifications are checked to ensure that there is no risk to personnel throughout the process.
Air compressors and other compressed air equipment, such as portable dryers and high-pressure boosters, are essential at this stage. They help maintain the required pressure during various tests and ensure that the pipeline operates within its intended parameters.
3. After use
monitoring the pipeline to ensure optimal performance and address any issues that may arise . Valuable data on system function, product movement, temperature, pressure readings and potential risks are collected and insights are provided for day-to-day management.
of mobile air compressors and monitoring equipment, operators can make necessary adjustments based on real-time data to ensure the continued efficiency and safety of the pipeline.
Pipeline pressure testing methods
hydrostatic testing, is an important step in ensuring the reliability and safety of pipelines before they are put into service. This test checks the maximum capacity of the pipeline, possible leaks, fittings, and pressure limits.
1. Hydrostatic test
Hydrostatic testing is the most common method for pressure testing. It involves filling a vessel with an incompressible fluid, such as water or oil, and subjecting it to pressures higher than its normal operating level.
This process helps to detect leaks or changes in the shape of the pipe. Dyes can be added to help detect leaks immediately. The pressure applied during the test is significantly higher than normal to account for unexpected pressure levels.
2. Pneumatic test
Pneumatic testing is another method that involves pressurizing the pipeline with air or inert gas to 110% of its design capacity . This method is suitable for low-pressure applications where fluids cannot be used. However, due to the high risk of system failure, pneumatic testing requires official approval from local authorities and guidance from expert engineers.
Special equipment for pipeline inspection
The use of specialized equipment such as portable air compressors, portable desiccant dryers, high pressure boosters and nitrogen generators is essential for pipeline commissioning to ensure safety and efficiency. Nitrogen is a safer alternative to compressed air when working with hazardous gases and helps maintain safety during the commissioning process .
portable dryers and high-pressure boosters, also plays a vital role in maintaining the required pressure and keeping the pipeline dry and free of contaminants. This equipment ensures that the pipeline is operating optimally from the start and continues to operate.
Frequently Asked Questions About Pipeline Inspection
What is pipeline commissioning and why is it important?
Pipeline commissioning is the process of ensuring that a newly constructed or modified pipeline system is ready for operation. It is important to prevent operational problems, leaks, and hazardous situations by thoroughly testing and cleaning the pipeline before use.
What are the typical steps in the pipeline inspection process?
The pipeline inspection process typically involves three phases: pre-commissioning, commissioning, and post-commissioning. These phases include preparing, testing, and monitoring the pipeline for optimal performance.
Why is special equipment needed to commission a pipeline?
To ensure safety and efficiency during pipeline commissioning, especially when hazardous gases are involved, specialized equipment such as portable air compressors, power generators, portable dryers, and nitrogen generators is needed.
Solution
Pipeline inspection is essential to ensuring the safety and efficiency of newly constructed or modified pipelines. The inspection process involves several stages, including pre-inspection, commissioning, and commissioning, where the pipeline is tested, cleaned, and filled with product. Special equipment such as portable air compressors, portable dryers, and boosters are often required to perform these inspections safely and efficiently. By understanding the importance of pipeline inspection and the various techniques involved, we can ensure the safety and reliability of our pipeline systems.